




- Details
-
EN 10255 is a European technical standard that specifies the requirements for non-alloy steel tubes suitable for welding and threading. These pipes are widely used for fluid transport and structural applications under low to medium pressure conditions.
Here is a detailed overview of its key aspects:
📌 Standard Overview and Scope
Full Title: Non-alloy steel tubes suitable for welding and threading - Technical delivery conditions .
Current Version: The latest version is EN 10255:2015, which supersedes the earlier editions EN 10255:2004 and EN 10255:2004+A1:2007 .
Evolution: This standard evolved from the British standard BS 1387:1985 and has been harmonized as a common European specification .
Scope: It applies to circular seamless and welded steel tubes with specified outside diameters ranging from 10.2 mm to 165.1 mm (corresponding to thread sizes from 1/8 inch to 6 inches) . These tubes are primarily intended for conveying fluids (like water, gas, and steam) in low-pressure systems and for non-load-bearing structural components .
⚙️ Technical Specifications
1. Dimensions and Classification
Tubes under this standard are typically classified into series based on wall thickness :
Medium Series (M): Thinner walls, used for general low-pressure fluid transport.
Heavy Series (H): Thicker walls, suitable for higher-pressure applications or mechanical structures.
Light Series (L): Mentioned in some references, with the thinnest walls for applications where weight is a concern .
Dimensional tolerances are strictly controlled, for example, the outside diameter tolerance is generally within ±0.75% to ±1% .
2. Material and Mechanical Properties
Common Steel Grade: S195T is the typical grade.
Chemical Composition: Features low-carbon content (Max Carbon: 0.20%-0.24%) to ensure good weldability and threading performance. Other elements are also controlled (e.g., Manganese ≤1.40%, Phosphorus ≤0.035%-0.045%, Sulfur ≤0.030%-0.045%) .
Mechanical Properties:
Upper Yield Strength (ReH): ≥195 MPa .
Tensile Strength (Rm): 320-520 MPa .
Elongation (A): ≥20% - 25% .

3. Surface Treatment and End Finishes
The tubes are available with various surface finishes and end preparations to suit different application needs :
Surface Treatments: Common options include black (bare finish), hot-dip galvanizing (for corrosion resistance), painting, and varnishing .
End Finishes: Can be supplied as Plain Ends (for welding), Screwed Ends (threaded), or Screwed and Socketed (S&S) for easy jointing .
🏭 Manufacturing and Quality Control
The production process involves key steps like raw material selection, forming, welding (for welded tubes), heat treatment, and surface finishing. Key quality control measures include :
Pressure Test: Each tube undergoes a hydrostatic or pneumatic pressure test at a minimum of 1.5 times the working pressure .
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Welded seams are inspected using methods like ultrasonic or radiographic testing .
Certification: Products can be accompanied by test certificates per EN 10204. For the EU market, CE marking under the Construction Products Regulation (CPR) is often required, following specific certification modules (e.g., Module 3 or 4) .
🏗️ Primary Applications
EN 10255 pipes are versatile and used across numerous industries :
Construction: Water supply, drainage, gas transmission within buildings, and structural supports .
Fluid Transport: Low-pressure systems for water, gas, air, and steam; also used in firefighting systems .
Industrial: Applications in the oil and gas (non-pressure/low-pressure), chemical (for non-corrosive media), and HVAC sectors .
Other Uses: Agricultural irrigation, electrical conduit protection, and scaffolding .
I hope this comprehensive overview is helpful. If you have more specific questions, such as regarding a particular application or a comparison with other standards, please feel free to ask.
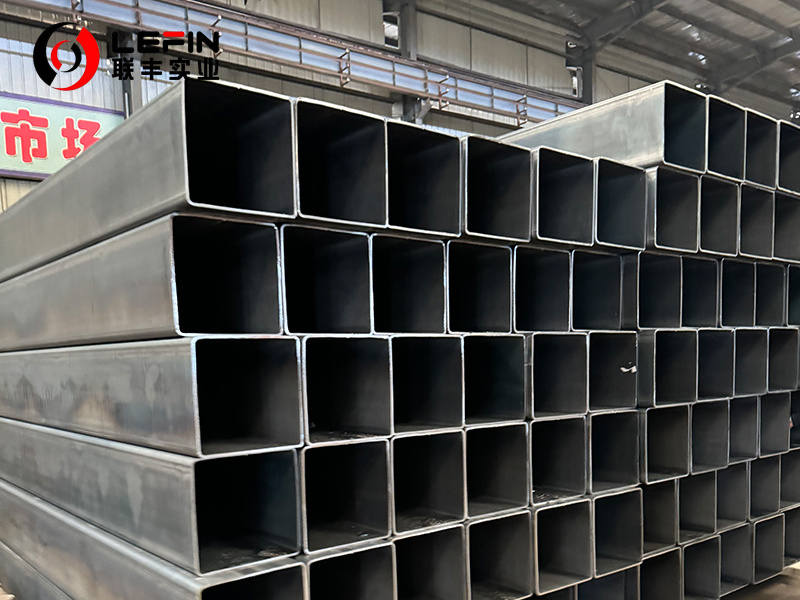

EN 10255 PIPE
Subcategory
Keyword
- Details
-
EN 10255 is a European technical standard that specifies the requirements for non-alloy steel tubes suitable for welding and threading. These pipes are widely used for fluid transport and structural applications under low to medium pressure conditions.
Here is a detailed overview of its key aspects:
📌 Standard Overview and Scope
Full Title: Non-alloy steel tubes suitable for welding and threading - Technical delivery conditions .
Current Version: The latest version is EN 10255:2015, which supersedes the earlier editions EN 10255:2004 and EN 10255:2004+A1:2007 .
Evolution: This standard evolved from the British standard BS 1387:1985 and has been harmonized as a common European specification .
Scope: It applies to circular seamless and welded steel tubes with specified outside diameters ranging from 10.2 mm to 165.1 mm (corresponding to thread sizes from 1/8 inch to 6 inches) . These tubes are primarily intended for conveying fluids (like water, gas, and steam) in low-pressure systems and for non-load-bearing structural components .

⚙️ Technical Specifications
1. Dimensions and Classification
Tubes under this standard are typically classified into series based on wall thickness :
Medium Series (M): Thinner walls, used for general low-pressure fluid transport.
Heavy Series (H): Thicker walls, suitable for higher-pressure applications or mechanical structures.
Light Series (L): Mentioned in some references, with the thinnest walls for applications where weight is a concern .
Dimensional tolerances are strictly controlled, for example, the outside diameter tolerance is generally within ±0.75% to ±1% .
2. Material and Mechanical Properties
Common Steel Grade: S195T is the typical grade.
Chemical Composition: Features low-carbon content (Max Carbon: 0.20%-0.24%) to ensure good weldability and threading performance. Other elements are also controlled (e.g., Manganese ≤1.40%, Phosphorus ≤0.035%-0.045%, Sulfur ≤0.030%-0.045%) .
Mechanical Properties:
Upper Yield Strength (ReH): ≥195 MPa .
Tensile Strength (Rm): 320-520 MPa .
Elongation (A): ≥20% - 25% .

3. Surface Treatment and End Finishes
The tubes are available with various surface finishes and end preparations to suit different application needs :
Surface Treatments: Common options include black (bare finish), hot-dip galvanizing (for corrosion resistance), painting, and varnishing .
End Finishes: Can be supplied as Plain Ends (for welding), Screwed Ends (threaded), or Screwed and Socketed (S&S) for easy jointing .
🏭 Manufacturing and Quality Control
The production process involves key steps like raw material selection, forming, welding (for welded tubes), heat treatment, and surface finishing. Key quality control measures include :
Pressure Test: Each tube undergoes a hydrostatic or pneumatic pressure test at a minimum of 1.5 times the working pressure .
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Welded seams are inspected using methods like ultrasonic or radiographic testing .
Certification: Products can be accompanied by test certificates per EN 10204. For the EU market, CE marking under the Construction Products Regulation (CPR) is often required, following specific certification modules (e.g., Module 3 or 4) .
🏗️ Primary Applications
EN 10255 pipes are versatile and used across numerous industries :
Construction: Water supply, drainage, gas transmission within buildings, and structural supports .
Fluid Transport: Low-pressure systems for water, gas, air, and steam; also used in firefighting systems .
Industrial: Applications in the oil and gas (non-pressure/low-pressure), chemical (for non-corrosive media), and HVAC sectors .
Other Uses: Agricultural irrigation, electrical conduit protection, and scaffolding .
I hope this comprehensive overview is helpful. If you have more specific questions, such as regarding a particular application or a comparison with other standards, please feel free to ask.

Related products
Product Consulting

Address: Hengtai Road,Daqiuzhuang Town,Jinghai County,Tianjin,China
Mob: +8615122229899(whatspp)
Phone: +86 22 58171905
Fax: +86 22 58171902
E-mail:info@lefinsteel.com
Get company updates

Tianjin Lefin Industrial Co.,Ltd. All rights reserved City sub-station SEO www.300.cn

