




- Details
-
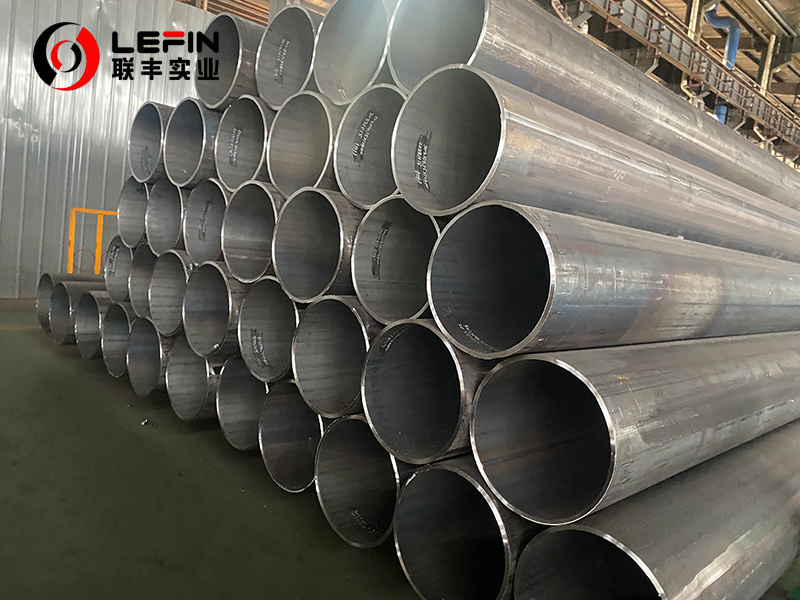
NZS 1163 HOLLOW SECTIONS usually refers to the AS/NZS 1163 "Cold-formed Structural Steel Hollow Sections" (a joint standard of Australia and New Zealand), which is the core specification for the production, performance and supply of cold-formed resistance-welded hollow sections with circular (CHS), square (SHS), and rectangular (RHS) cross-sections in New Zealand and Australia.
It is mainly used in general structures and engineering scenarios. The following provides a detailed explanation from the aspects of definition, core requirements, and application.
I. Core Definition and Scope of Application
- Essence:Jointly issued by the Standards New Zealand and the Australian Standards Authority, the current valid version is AS/NZS 1163:2016, replacing the previous version 2009/1991.
- Applicable Products:Cold-formed, resistance-welded carbon steel hollow sections, excluding submerged arc welding, spiral welding or UO forming products; and limited to structural steel after cold bending without subsequent heat treatment.
- Section Types:Circular (CHS), square (SHS), rectangular (RHS) hollow sections, covering from smaller specifications to large structural sections.
II. Key Considerations (Critical Technical Points)
1. Strength Grades and Impact Properties
The standard defines 3 strength grades, with the suffix "L0" indicating guaranteed 0°C impact toughness. There are 6 commonly used grades, as follows:Grade Minimum Yield Strength ReH (MPa) Minimum Tensile Strength Rm (MPa) Impact Properties C250 250 320 Not guaranteed C250L0 250 320 0°C Impact Compliance C350 350 430 Not guaranteed C350L0 350 430 0°C Impact Compliance C450 450 500 Not guaranteed C450L0 450 500 0°C Impact Compliance
2. Manufacturing and Quality Control
- Process Specifications:Cold bending forming + resistance welding. Clearly define the requirements for forming, welding, and surface treatment, emphasizing no subsequent heat treatment.
- Key Indicators:Strictly stipulate chemical composition, dimensional tolerances (outer diameter/edge length, wall thickness), mechanical properties (yield, tensile strength, elongation), weld quality, impact toughness (L0 grade), and surface quality.
- Testing and Traceability:Must undergo type testing and factory production control, providing complete material certificates and traceability documents.
- Connection Compatibility:Welding should comply with the AS/NZS 1554 series, and fastening should refer to AS 3990, AS 4100, NZS 3404, etc. standards.
3. Section Characteristics and Design Basis
- Appendix D provides the nominal dimensions, section characteristics (area, moment of inertia, section modulus) and theoretical weight of common sections; dimensions not listed can be calculated using the formulas in Appendix E.
- The design should be based on standards such as AS 4100 (Steel Structures) and AS/NZS 4600 (Cold-Formed Steel Structures) to ensure structural safety.
III. Typical Application Scenarios
1. Architecture and Civil Structures
- Building frames, columns, beams, trusses, support systems, especially suitable for multi-story and large-span steel structures.
- Infrastructure such as bridges, municipal guardrails, lamp posts, traffic sign posts, pipe truss bridges, etc.
- Prefabricated steel structures, modular buildings, storage shelves, agricultural greenhouses, etc.
2. Mechanical and Industrial Applications
- Load-bearing components of engineering machinery chassis, frames, legs, booms, etc.
- Equipment frames and pipe supports in industries such as mining, power, water treatment, etc.
- Steel structures for amusement facilities, sports venues, curtain wall ribs, etc.
3. Selection and Usage Tips
- Select the grade based on load: generally C250 for general load-bearing, C350 for medium load, C450 for heavy load or high stress; L0 grade is preferred for low-temperature environments.
- Check dimensions and supply capacity: some specifications may be limited by production capacity, and it is necessary to confirm market supply before design.
- Welding and Corrosion Prevention: Follow the corresponding welding standards and adopt coating, hot-dip galvanizing and other anti-corrosion measures according to the environment.IV. Summary
AS/NZS 1163 is the core specification for cold-formed resistance welded hollow sections in the Australian and New Zealand region. By clearly defining the grades, properties, manufacturing and quality requirements, it ensures structural safety and connection compatibility, and is widely used in fields such as construction, bridges, and machinery. The selection should be based on the load, environment and connection method to ensure compliance and reliability.

NZS 1163 HOLLOW SECTIONS
Subcategory
Keyword
- Details
-
NZS 1163 HOLLOW SECTIONS usually refers to the AS/NZS 1163 "Cold-formed Structural Steel Hollow Sections" (a joint standard of Australia and New Zealand), which is the core specification for the production, performance and supply of cold-formed resistance-welded hollow sections with circular (CHS), square (SHS), and rectangular (RHS) cross-sections in New Zealand and Australia.
It is mainly used in general structures and engineering scenarios. The following provides a detailed explanation from the aspects of definition, core requirements, and application.
I. Core Definition and Scope of Application
- Essence:Jointly issued by the Standards New Zealand and the Australian Standards Authority, the current valid version is AS/NZS 1163:2016, replacing the previous version 2009/1991.
- Applicable Products:Cold-formed, resistance-welded carbon steel hollow sections, excluding submerged arc welding, spiral welding or UO forming products; and limited to structural steel after cold bending without subsequent heat treatment.
- Section Types:Circular (CHS), square (SHS), rectangular (RHS) hollow sections, covering from smaller specifications to large structural sections.
II. Key Considerations (Critical Technical Points)
1. Strength Grades and Impact Properties
The standard defines 3 strength grades, with the suffix "L0" indicating guaranteed 0°C impact toughness. There are 6 commonly used grades, as follows:Grade Minimum Yield Strength ReH (MPa) Minimum Tensile Strength Rm (MPa) Impact Properties C250 250 320 Not guaranteed C250L0 250 320 0°C Impact Compliance C350 350 430 Not guaranteed C350L0 350 430 0°C Impact Compliance C450 450 500 Not guaranteed C450L0 450 500 0°C Impact Compliance
2. Manufacturing and Quality Control
- Process Specifications:Cold bending forming + resistance welding. Clearly define the requirements for forming, welding, and surface treatment, emphasizing no subsequent heat treatment.
- Key Indicators:Strictly stipulate chemical composition, dimensional tolerances (outer diameter/edge length, wall thickness), mechanical properties (yield, tensile strength, elongation), weld quality, impact toughness (L0 grade), and surface quality.
- Testing and Traceability:Must undergo type testing and factory production control, providing complete material certificates and traceability documents.
- Connection Compatibility:Welding should comply with the AS/NZS 1554 series, and fastening should refer to AS 3990, AS 4100, NZS 3404, etc. standards.
3. Section Characteristics and Design Basis
- Appendix D provides the nominal dimensions, section characteristics (area, moment of inertia, section modulus) and theoretical weight of common sections; dimensions not listed can be calculated using the formulas in Appendix E.
- The design should be based on standards such as AS 4100 (Steel Structures) and AS/NZS 4600 (Cold-Formed Steel Structures) to ensure structural safety.
III. Typical Application Scenarios
1. Architecture and Civil Structures
- Building frames, columns, beams, trusses, support systems, especially suitable for multi-story and large-span steel structures.
- Infrastructure such as bridges, municipal guardrails, lamp posts, traffic sign posts, pipe truss bridges, etc.
- Prefabricated steel structures, modular buildings, storage shelves, agricultural greenhouses, etc.
2. Mechanical and Industrial Applications
- Load-bearing components of engineering machinery chassis, frames, legs, booms, etc.
- Equipment frames and pipe supports in industries such as mining, power, water treatment, etc.
- Steel structures for amusement facilities, sports venues, curtain wall ribs, etc.
3. Selection and Usage Tips
- Select the grade based on load: generally C250 for general load-bearing, C350 for medium load, C450 for heavy load or high stress; L0 grade is preferred for low-temperature environments.
- Check dimensions and supply capacity: some specifications may be limited by production capacity, and it is necessary to confirm market supply before design.
- Welding and Corrosion Prevention: Follow the corresponding welding standards and adopt coating, hot-dip galvanizing and other anti-corrosion measures according to the environment.IV. Summary
AS/NZS 1163 is the core specification for cold-formed resistance welded hollow sections in the Australian and New Zealand region. By clearly defining the grades, properties, manufacturing and quality requirements, it ensures structural safety and connection compatibility, and is widely used in fields such as construction, bridges, and machinery. The selection should be based on the load, environment and connection method to ensure compliance and reliability.

Related products
Product Consulting

Address: Hengtai Road,Daqiuzhuang Town,Jinghai County,Tianjin,China
Mob: +8615122229899(whatspp)
Phone: +86 22 58171905
Fax: +86 22 58171902
E-mail:info@lefinsteel.com
Get company updates

Tianjin Lefin Industrial Co.,Ltd. All rights reserved City sub-station SEO www.300.cn

