
- Details
-
ASTM A53 seamless steel pipe is a kind of carbon steel pipe widely used in the industrial field. Below, I will provide you with a detailed interpretation from aspects such as its advantages, applications, specific requirements of standards and production processes.
🔍 ASTM A53 seamless steel pipe overview
ASTM A53 is a standard formulated by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), covering seamless and welded black pipes and hot-dip galvanized steel pipes.
Among them, seamless steel pipes (Type S) have significant advantages in reliability and strength due to the characteristics of their manufacturing processes, and are often used in critical pressure systems and structural components.
✨ Core strengths and features
The core advantage of seamless steel pipes lies in their outstanding mechanical properties and structural integrity:
High strength and pressure resistance:
Especially for Grade B, its minimum tensile strength is ≥415 MPa and the minimum yield strength is ≥240 MPa, which is much higher than that of ordinary low-carbon steel pipes. It can withstand the transportation tasks of high-pressure fluids (such as oil and gas at 5-10 mpa).
As there are no weld seams, its strength is uniform, reducing the risk of local stress concentration
Outstanding durability and safety:
The seamless structure eliminates potential defects in welds, enhancing reliability and safety under high pressure, extreme temperatures or corrosive environments
Its elongation is usually ≥24%, and can even reach 30%, which means that it can absorb energy through plastic deformation when overloaded, avoiding sudden brittle fracture.
Good processability and economy:
Although the initial cost may be higher than that of welded pipes, its long service life, low maintenance requirements and wide applicability (which can enhance anti-corrosion through coating and galvanizing) bring good long-term economy
🏗️ Main application fields
The characteristics of ASTM A53 seamless steel pipes make them indispensable in multiple fields:
Petroleum and natural gas industry:
Pipelines used for transporting high-pressure fluids such as oil and gas
Architectural and Structural Engineering:
Steel beams, supports, scaffolds and other structural components suitable for large-span buildings
Public utilities and fluid transportation:
Widely used in water supply, heating (such as boiler pipelines), fire protection systems, etc
Mechanical manufacturing and special purposes:
It is used for manufacturing mechanical components such as bearing sleeves and hydraulic cylinder barrels, as well as for special occasions like anti-static pipes in wind power plants
📋 Standard requirements (numerical details)
ASTM A53 standard has clear regulations on chemical composition, mechanical properties, dimensions, etc. It is mainly divided into two grades: Grade A and Grade B. Among them, Grade B has higher requirements and is more widely applied.
Indicator item Grade A Grade B Chemical composition Carbon (C) ≤0.25% ,
Manganese (Mn)≤ 0.95%,
Phosphorus (P)≤0.05% ,
Sulphur (S) ≤0.045%
Carbon (C)≤0.30% ,
Panganese (Mn)≤1.20% ,
Phosphorus (P)≤ 0.05%,
Sulphur (S)≤0.045%
Tensile strength ≥330 MPa ≥415 MPa Yield strength ≥205 MPa ≥240 MPa Elongation Calculate according to the formula(related to the cross-sectional area and tensile strength of the specimen) Calculate according to the formula (related to the cross-sectional area and tensile strength of the specimen)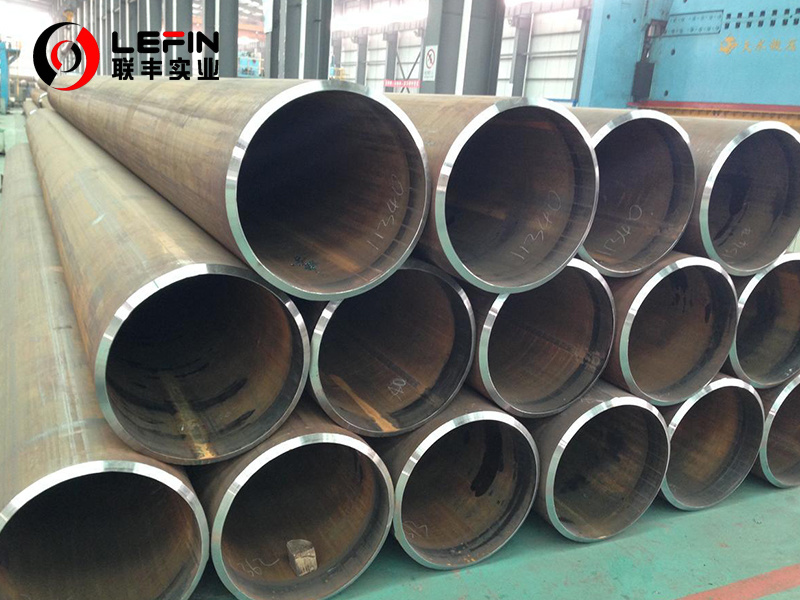 
💡Dimensions and tolerances
Outer diameter range:
Typically covers approximately 1/8 inch to 26 inches (or approximately 13.7 mm to 812.8 mm)
Wall thickness:
The common range of wall thickness is from a few millimeters to tens of millimeters (such as 1-50mm)
Or 6-30mm. It depends on the pipe number (Sch).Length:
Usually 5.8 meters to 12 meters, with no fixed length.
Allowable deviation of outer diameter(OD):
For example, ±0.40mm when the outer diameter is ≤48.3mm; When the outer diameter is ≥60.3mm, it is ±1%.
Allowable deviation of wall thickness(WT):
usually ±12.5% of the nominal wall thickness.
Other requirements:
The standard also includes flattening tests and cold bending tests (for example, for steel pipes with a diameter of ≤60.3mm, the bending core diameter should be 12D, and there should be no cracks when bent at 90°).
Such as hydrostatic testing or non-destructive testing (such as ultrasonic flaw detection), etc., to ensure quality.
ASTM A53 SEAMLESS STEEL PIPE
Subcategory
Keyword
- Details
-
ASTM A53 seamless steel pipe is a kind of carbon steel pipe widely used in the industrial field. Below, I will provide you with a detailed interpretation from aspects such as its advantages, applications, specific requirements of standards and production processes.
🔍 ASTM A53 seamless steel pipe overview
ASTM A53 is a standard formulated by the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM), covering seamless and welded black pipes and hot-dip galvanized steel pipes.
Among them, seamless steel pipes (Type S) have significant advantages in reliability and strength due to the characteristics of their manufacturing processes, and are often used in critical pressure systems and structural components.
✨ Core strengths and features
The core advantage of seamless steel pipes lies in their outstanding mechanical properties and structural integrity:
High strength and pressure resistance:
Especially for Grade B, its minimum tensile strength is ≥415 MPa and the minimum yield strength is ≥240 MPa, which is much higher than that of ordinary low-carbon steel pipes. It can withstand the transportation tasks of high-pressure fluids (such as oil and gas at 5-10 mpa).
As there are no weld seams, its strength is uniform, reducing the risk of local stress concentration
Outstanding durability and safety:
The seamless structure eliminates potential defects in welds, enhancing reliability and safety under high pressure, extreme temperatures or corrosive environments
Its elongation is usually ≥24%, and can even reach 30%, which means that it can absorb energy through plastic deformation when overloaded, avoiding sudden brittle fracture.
Good processability and economy:
Although the initial cost may be higher than that of welded pipes, its long service life, low maintenance requirements and wide applicability (which can enhance anti-corrosion through coating and galvanizing) bring good long-term economy

🏗️ Main application fields
The characteristics of ASTM A53 seamless steel pipes make them indispensable in multiple fields:
Petroleum and natural gas industry:
Pipelines used for transporting high-pressure fluids such as oil and gas
Architectural and Structural Engineering:
Steel beams, supports, scaffolds and other structural components suitable for large-span buildings
Public utilities and fluid transportation:
Widely used in water supply, heating (such as boiler pipelines), fire protection systems, etc
Mechanical manufacturing and special purposes:
It is used for manufacturing mechanical components such as bearing sleeves and hydraulic cylinder barrels, as well as for special occasions like anti-static pipes in wind power plants
📋 Standard requirements (numerical details)
ASTM A53 standard has clear regulations on chemical composition, mechanical properties, dimensions, etc. It is mainly divided into two grades: Grade A and Grade B. Among them, Grade B has higher requirements and is more widely applied.
Indicator item Grade A Grade B Chemical composition Carbon (C) ≤0.25% ,
Manganese (Mn)≤ 0.95%,
Phosphorus (P)≤0.05% ,
Sulphur (S) ≤0.045%
Carbon (C)≤0.30% ,
Panganese (Mn)≤1.20% ,
Phosphorus (P)≤ 0.05%,
Sulphur (S)≤0.045%
Tensile strength ≥330 MPa ≥415 MPa Yield strength ≥205 MPa ≥240 MPa Elongation Calculate according to the formula(related to the cross-sectional area and tensile strength of the specimen) Calculate according to the formula (related to the cross-sectional area and tensile strength of the specimen) 
💡Dimensions and tolerances
Outer diameter range:
Typically covers approximately 1/8 inch to 26 inches (or approximately 13.7 mm to 812.8 mm)
Wall thickness:
The common range of wall thickness is from a few millimeters to tens of millimeters (such as 1-50mm)
Or 6-30mm. It depends on the pipe number (Sch).Length:
Usually 5.8 meters to 12 meters, with no fixed length.
Allowable deviation of outer diameter(OD):
For example, ±0.40mm when the outer diameter is ≤48.3mm; When the outer diameter is ≥60.3mm, it is ±1%.
Allowable deviation of wall thickness(WT):
usually ±12.5% of the nominal wall thickness.
Other requirements:
The standard also includes flattening tests and cold bending tests (for example, for steel pipes with a diameter of ≤60.3mm, the bending core diameter should be 12D, and there should be no cracks when bent at 90°).
Such as hydrostatic testing or non-destructive testing (such as ultrasonic flaw detection), etc., to ensure quality.
Related products
Product Consulting

Address: Hengtai Road,Daqiuzhuang Town,Jinghai County,Tianjin,China
Mob: +8615122229899(whatspp)
Phone: +86 22 58171905
Fax: +86 22 58171902
E-mail:info@lefinsteel.com
Get company updates

Tianjin Lefin Industrial Co.,Ltd. All rights reserved City sub-station SEO www.300.cn

