



- Details
-
Standard: ASTM A53
ASTM A53 and ASME SA53 is intended for Pressure service (e.g., steam, water, compressed air, hydrocarbon gases within temperature limits) and Structural applications (e.g., scaffolding, handrails, support piling). It is suitable for welding and for forming operations involving coiling, bending, and flanging, subject to certain qualifications.A53 covers Seamless and Welded, Black and Hot-Dipped Galvanized nominal (average) wall pipe for coiling, bending, flanging and other special purposes and is suitable for welding. Continuous-Welded pipe is not intended for flanging. Purpose for which pipe is intended should be stated on order.
Key Manufacturing Types
Type S (Seamless): Produced via hot piercing/extrusion. Highest integrity for critical services.
Type E (ERW - Electric Resistance Welded): Roll-formed and fusion-welded without filler metal. Cost-effective for mid-range pressures.
Type F (Furnace Butt-Welded): Continuously welded using forge pressure. Limited to lighter walls (typically Sch 10 or thinner) and Grade A.
Material Grades
Grade A: Minimum tensile strength 330 MPa (48 ksi), yield 205 MPa (30 ksi). Common for structural/low-pressure uses.
Grade B: Enhanced mechanicals – tensile 415 MPa (60 ksi), yield 240 MPa (35 ksi). Preferred for pressure piping systems.
Surface Treatment Options:
Black (Bare): Uncoated with residual mill scale. Requires external corrosion protection in service.
Galvanized (Zinc-Coated): Hot-dip processed post-manufacture. Standard for corrosion-prone environments like fencing or water lines.
Sizes Range Of A/SA53-B Seamless And Welded Pipe In:
Sizes: 1/8" NPS to 26" OD
Schedules: S/10, S/20, S/40, STD, S/60, S/80, XH, S/100, S/120, S/140, S/160 and XXH
Chemical Requirements
Type S
(seamless)Type E Type F (electric-
resistance welded)(furnace-
welded pipe)Element Grade A Grade B Grade A Grade B Grade A Carbon max. % 0.25 0.30* 0.25 0.30* 0.3 Manganese % 0.95 1.2 0.95 1.2 1.2 Phosphorous, max. % 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 Sulfur, max. % 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 Copper, max.% 0.40 0.40 0.40 0.40 0.4 Nickel, max. % 0.40 0.40 0.40 0.40 0.4 Chromium, max. % 0.40 0.40 0.40 0.40 0.4 Molybdenum, max. % 0.15 0.15 0.15 0.15 0.15 Vanadium, max. % 0.08 0.08 0.08 0.08 0.08 *For each reduction below 0.01% below the specified carbon maximum, an increase of 0.06% manganese above the specified maximum will be permitted up to a maximum of 1.65% (does not apply to SA53).
Key Elements: Primarily Iron (Fe), Carbon (C), Manganese (Mn), with traces of Phosphorus (P), Sulfur (S), Copper (Cu), Nickel (Ni), Chromium (Cr), Molybdenum (Mo), and Vanadium (V) within specified limits.Grade B Difference: Generally has slightly higher Carbon and Manganese content than Grade A to achieve higher strength.
Mechanical Properties
Seamless and Electric-resistance-welded Continuous-Welded
Grade A Grade B
Tensile Strength, min., psi 48,000 60,000 45,000 Yield Strength, min., psi 30,000 35,000 25,000
Elongation: Varies based on specimen size and wall thickness, typically ranging from 35% down to around 15% for heavier walls.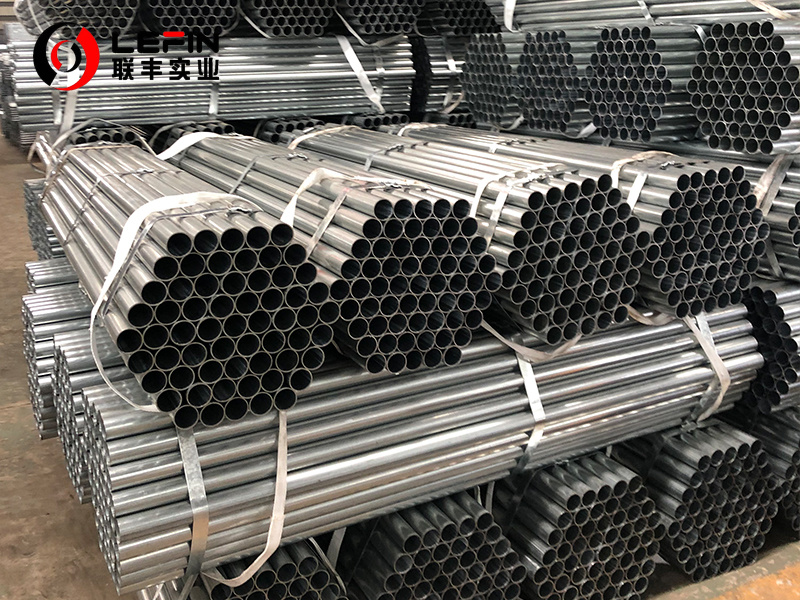
Testing Requirements
Hydrostatic Test: Mandatory for all pipe unless replaced by NDE for seamless (Type S). Test pressure calculated per formula in the standard (typically generates stress ≥ 1000 psi / 6.9 MPa in the pipe wall).Non-Destructive Electric Test (NDE): Mandatory for ERW (Type E) and Seamless (Type S) pipe. Ensures weld integrity (ERW) or detects imperfections (Seamless). Methods include eddy current or ultrasonic testing. Can replace hydrostatic test for seamless pipe.
Flattening Test (Welded Pipe): Required for ERW (Type E) to demonstrate weld ductility.
Bend Test (Furnace Welded): Required for Type F.
Tensile Test: Required per lot.
Hardness Test: May be required for certain supplementary requirements.
Coating Tests (Galvanized): Zinc adherence (hammer or vise test) and coating weight (triple-spot test).
Limitations & Notes
Not for High-Temperature Service: Not intended for use above 430°C (800°F). ASTM A106 is the preferred specification for seamless carbon steel pipe for high-temperature service.Not for Severe Corrosion: Primarily for mild environments; galvanizing provides limited corrosion protection.
Weldability: Generally good due to low carbon content.
Pressure Rating: Actual working pressure depends on size, schedule (wall thickness), grade, temperature, and design code (e.g., ASME B31.1, B31.3).
Applications
Low/Medium Pressure Piping Systems: Water distribution, compressed air, steam (low-pressure), gas (natural gas, propane - subject to local codes), oil lines.
Structural Applications: Scaffolding, handrails, fencing, guardrails, support posts.
Conduit: Electrical conduit (often galvanized).
General Fabrication: Frames, equipment bases.
Q And A
Q1: Can ASTM A53 Grade B Pipe Replace ASTM A106 Pipe In High-Temperature Service?
A: Not recommended. While both are carbon steel pipes:A53 is rated for ≤430°C (800°F) – its mechanical properties degrade beyond this threshold.
A106 (specifically for high-temp service) maintains strength up to 485°C (900°F) due to stricter chemistry controls (e.g., lower sulfur/phosphorus).
Critical difference: A106 seamless pipe undergoes normalization heat treatment for enhanced grain structure stability. Substituting A53 in steam lines >430°C risks creep failure or weld cracking.Q2: Why Is ERW (Type E) ASTM A53 Pipe Sometimes Rejected For Sour Service Pipelines?
A: Primarily due to weld integrity risks in H₂S environments:Selective Corrosion: ERW heat-affected zones (HAZ) are prone to sulfide stress cracking (SSC) if hardness exceeds 22 HRC (per NACE MR0175).
Lack of Normalization: "As-welded" ERW pipes retain residual stresses, increasing SSC susceptibility vs normalized seamless pipe.
Defect Sensitivity: Incomplete fusion flaws at the weld seam can become crack initiation points under sour gas exposure.
Summary
ASTM A53 is a fundamental specification for carbon steel pipe, available in seamless (Type S), electric-resistance welded (Type E), and furnace-butt welded (Type F) forms, in Grades A (lower strength) and B (higher strength). It is widely used for pressure piping, structural applications, and general purpose use. Pipe can be supplied bare (black) or galvanized. Key requirements include chemistry, mechanical properties, dimensional compliance, mandatory hydrostatic or NDE testing, and specific marking. While versatile, it is not suitable for high-temperature service or highly corrosive environments. Grade B, Type S or E is the most common choice for general pressure piping.

ASTM A53 Pipe
Subcategory
Keyword
- Details
-
Standard: ASTM A53
ASTM A53 and ASME SA53 is intended for Pressure service (e.g., steam, water, compressed air, hydrocarbon gases within temperature limits) and Structural applications (e.g., scaffolding, handrails, support piling). It is suitable for welding and for forming operations involving coiling, bending, and flanging, subject to certain qualifications.A53 covers Seamless and Welded, Black and Hot-Dipped Galvanized nominal (average) wall pipe for coiling, bending, flanging and other special purposes and is suitable for welding. Continuous-Welded pipe is not intended for flanging. Purpose for which pipe is intended should be stated on order.
Key Manufacturing Types
Type S (Seamless): Produced via hot piercing/extrusion. Highest integrity for critical services.
Type E (ERW - Electric Resistance Welded): Roll-formed and fusion-welded without filler metal. Cost-effective for mid-range pressures.
Type F (Furnace Butt-Welded): Continuously welded using forge pressure. Limited to lighter walls (typically Sch 10 or thinner) and Grade A.
Material Grades
Grade A: Minimum tensile strength 330 MPa (48 ksi), yield 205 MPa (30 ksi). Common for structural/low-pressure uses.
Grade B: Enhanced mechanicals – tensile 415 MPa (60 ksi), yield 240 MPa (35 ksi). Preferred for pressure piping systems.
Surface Treatment Options:
Black (Bare): Uncoated with residual mill scale. Requires external corrosion protection in service.
Galvanized (Zinc-Coated): Hot-dip processed post-manufacture. Standard for corrosion-prone environments like fencing or water lines.
Sizes Range Of A/SA53-B Seamless And Welded Pipe In:
Sizes: 1/8" NPS to 26" OD
Schedules: S/10, S/20, S/40, STD, S/60, S/80, XH, S/100, S/120, S/140, S/160 and XXH

Chemical Requirements
Type S
(seamless)Type E Type F (electric-
resistance welded)(furnace-
welded pipe)Element Grade A Grade B Grade A Grade B Grade A Carbon max. % 0.25 0.30* 0.25 0.30* 0.3 Manganese % 0.95 1.2 0.95 1.2 1.2 Phosphorous, max. % 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 0.05 Sulfur, max. % 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 0.045 Copper, max.% 0.40 0.40 0.40 0.40 0.4 Nickel, max. % 0.40 0.40 0.40 0.40 0.4 Chromium, max. % 0.40 0.40 0.40 0.40 0.4 Molybdenum, max. % 0.15 0.15 0.15 0.15 0.15 Vanadium, max. % 0.08 0.08 0.08 0.08 0.08 *For each reduction below 0.01% below the specified carbon maximum, an increase of 0.06% manganese above the specified maximum will be permitted up to a maximum of 1.65% (does not apply to SA53).
Key Elements: Primarily Iron (Fe), Carbon (C), Manganese (Mn), with traces of Phosphorus (P), Sulfur (S), Copper (Cu), Nickel (Ni), Chromium (Cr), Molybdenum (Mo), and Vanadium (V) within specified limits.Grade B Difference: Generally has slightly higher Carbon and Manganese content than Grade A to achieve higher strength.
Mechanical Properties
Seamless and Electric-resistance-welded Continuous-Welded
Grade A Grade B
Tensile Strength, min., psi 48,000 60,000 45,000 Yield Strength, min., psi 30,000 35,000 25,000
Elongation: Varies based on specimen size and wall thickness, typically ranging from 35% down to around 15% for heavier walls.
Testing Requirements
Hydrostatic Test: Mandatory for all pipe unless replaced by NDE for seamless (Type S). Test pressure calculated per formula in the standard (typically generates stress ≥ 1000 psi / 6.9 MPa in the pipe wall).Non-Destructive Electric Test (NDE): Mandatory for ERW (Type E) and Seamless (Type S) pipe. Ensures weld integrity (ERW) or detects imperfections (Seamless). Methods include eddy current or ultrasonic testing. Can replace hydrostatic test for seamless pipe.
Flattening Test (Welded Pipe): Required for ERW (Type E) to demonstrate weld ductility.
Bend Test (Furnace Welded): Required for Type F.
Tensile Test: Required per lot.
Hardness Test: May be required for certain supplementary requirements.
Coating Tests (Galvanized): Zinc adherence (hammer or vise test) and coating weight (triple-spot test).
Limitations & Notes
Not for High-Temperature Service: Not intended for use above 430°C (800°F). ASTM A106 is the preferred specification for seamless carbon steel pipe for high-temperature service.Not for Severe Corrosion: Primarily for mild environments; galvanizing provides limited corrosion protection.
Weldability: Generally good due to low carbon content.
Pressure Rating: Actual working pressure depends on size, schedule (wall thickness), grade, temperature, and design code (e.g., ASME B31.1, B31.3).
Applications
Low/Medium Pressure Piping Systems: Water distribution, compressed air, steam (low-pressure), gas (natural gas, propane - subject to local codes), oil lines.
Structural Applications: Scaffolding, handrails, fencing, guardrails, support posts.
Conduit: Electrical conduit (often galvanized).
General Fabrication: Frames, equipment bases.
Q And A
Q1: Can ASTM A53 Grade B Pipe Replace ASTM A106 Pipe In High-Temperature Service?
A: Not recommended. While both are carbon steel pipes:A53 is rated for ≤430°C (800°F) – its mechanical properties degrade beyond this threshold.
A106 (specifically for high-temp service) maintains strength up to 485°C (900°F) due to stricter chemistry controls (e.g., lower sulfur/phosphorus).
Critical difference: A106 seamless pipe undergoes normalization heat treatment for enhanced grain structure stability. Substituting A53 in steam lines >430°C risks creep failure or weld cracking.Q2: Why Is ERW (Type E) ASTM A53 Pipe Sometimes Rejected For Sour Service Pipelines?
A: Primarily due to weld integrity risks in H₂S environments:Selective Corrosion: ERW heat-affected zones (HAZ) are prone to sulfide stress cracking (SSC) if hardness exceeds 22 HRC (per NACE MR0175).
Lack of Normalization: "As-welded" ERW pipes retain residual stresses, increasing SSC susceptibility vs normalized seamless pipe.
Defect Sensitivity: Incomplete fusion flaws at the weld seam can become crack initiation points under sour gas exposure.
Summary
ASTM A53 is a fundamental specification for carbon steel pipe, available in seamless (Type S), electric-resistance welded (Type E), and furnace-butt welded (Type F) forms, in Grades A (lower strength) and B (higher strength). It is widely used for pressure piping, structural applications, and general purpose use. Pipe can be supplied bare (black) or galvanized. Key requirements include chemistry, mechanical properties, dimensional compliance, mandatory hydrostatic or NDE testing, and specific marking. While versatile, it is not suitable for high-temperature service or highly corrosive environments. Grade B, Type S or E is the most common choice for general pressure piping.

Related products
Product Consulting

Address: Hengtai Road,Daqiuzhuang Town,Jinghai County,Tianjin,China
Mob: +8615122229899(whatspp)
Phone: +86 22 58171905
Fax: +86 22 58171902
E-mail:info@lefinsteel.com
Get company updates

Tianjin Lefin Industrial Co.,Ltd. All rights reserved City sub-station SEO www.300.cn

