



- Details
-
General Overview
S355 is a European structural steel grade with a minimum yield strength of 355 MPa at ≤16mm thickness.Subgrades (JR, J0H, J2H) indicate impact toughness requirements at different temperatures:
S355JR: Room temperature (20°C impact test).
S355J0H: 0°C impact test.
S355J2H: -20°C impact test.
The "H" in J0H/J2H denotes hollow sections (applies to EN 10219 cold-formed pipes).
Key Differences: EN 10210 Vs. EN 10219
Parameter
EN 10210 (Hot-Finished)
EN 10219 (Cold-Formed)
Manufacturing
Hot-formed, seamless or welded.
Cold-formed, welded (from coiled sheet).
Dimensional Tolerance
Tighter tolerances (better surface finish).
Slightly looser tolerances.
Mechanical Properties
Higher ductility (hot-working preserves grain structure).
Slightly lower ductility (cold-work hardening).
Impact Toughness
Generally better due to hot-forming process.
May require stricter testing for cold-formed variants.
Applications
Heavy-load structures (e.g., bridges, buildings).
Light-to-medium load (e.g., frames, supports).

Chemical Composition (Common For All S355 Grades)
Carbon (C): ≤0.22%.
Silicon (Si): ≤0.55%.
Manganese (Mn): ≤1.60%.
Phosphorus (P):EN 10210: ≤0.035%(J0H), ≤0.030%(J2H);
EN 10219: ≤0.040%(J0H), ≤0.035%(J2H);
Sulfur (S):
EN 10210: ≤0.035%(J0H), ≤0.030%(J2H);
EN 10219: ≤0.040%(J0H), ≤0.035%(J2H);
Micro alloys (Nb, V, Ti): Optional for grain refinement (especially in J2H).
Note: Both EN 10210 (hot-finished) and EN 10219 (cold-formed) S355 steel pipes have similar carbon, manganese, and impurity limits. However, EN 10219 may require stricter control of residuals (e.g., nitrogen) for better cold-forming.
Mechanical Properties (Typical Values)Grade
Yield Strength (MPa)
Nominal thickness≤16mmTensile Strength (MPa)
Nominal thickness >3≤40Elongation (%)
Nominal thickness≤40mmImpact Energy (J)
S355JR
≥355
470–630 (EN10210)
490–630 (EN10219)
≥22 (EN10210)
≥20 (EN10219)
≥27 J at 20°C
S355J0H
≥355
470–630 (EN10210)
490–630 (EN10219)
≥22 (EN10210)
≥20 (EN10219)
≥27 J at 0°C
S355J2H
≥355
470–630 (EN10210)
490–630 (EN10219)
≥22 (EN10210)
≥20 (EN10219)
≥27 J at -20°C
Note: EN 10210 offers higher ductility due to hot-forming, while EN 10219 has slightly higher strength from cold-work hardening. EN 10219 also includes low-temperature grades (J0H/J2H) for cold climates.
Hot vs. Cold Differences:
● Hot-finished (EN 10210): Typically show higher elongation (better ductility), better for heavy loads.● Cold-formed (EN 10219): More cost-effective, have higher tensile strength with options for cold resistance.

Applications And Advantages
EN 10210 Hot-Finished Pipes:
● Applications: Critical structural components (building frames, bridges, offshore platforms), heavy machinery, and high-stress welded constructions.
● Advantages:
Excellent weldability and formability due to homogeneous microstructureSuperior fatigue resistance and fracture toughness
Better dimensional accuracy and surface finish
Ideal for dynamic loading conditions
EN 10219 Cold-Formed Pipes:
● Applications: Light-to-medium structural applications (scaffolding, storage racks, agricultural equipment), architectural elements, and cost-sensitive projects.
● Advantages:
Higher yield strength from cold-workingMore economical for mass production
Available in precise, complex cross-sections
Low-temperature grades (J0H/J2H) perform well in cold climates
Summary And Selection Guidelines
S355-grade steel pipes under EN 10210 (hot-finished) and EN 10219 (cold-formed) standards offer distinct advantages tailored to different structural requirements.● EN 10210 pipes excel in heavy-load, high-integrity applications due to their superior ductility, impact toughness, and weldability from the hot-forming process. They are the preferred choice for critical structures like bridges, high-rise buildings, and offshore platforms where dynamic loading and fatigue resistance are crucial.
● EN 10219 pipes, on the other hand, provide cost-effective solutions for light-to-medium structural applications, with the added benefit of cold-work-enhanced strength and specialized low-temperature grades (J0H/J2H). Their precise forming capabilities make them ideal for architectural elements, storage systems, and projects requiring complex cross-sections.
Key Selection Criteria:
● Choose EN 10210 when structural integrity, weld performance, and dynamic load resistance are priorities.
● Opt for EN 10219 for budget-conscious projects, standardized components, or cold-environment applications.
Both standards maintain the core S355 mechanical properties but optimize them for different manufacturing processes and end uses, allowing engineers to select the most appropriate solution based on project-specific demands.
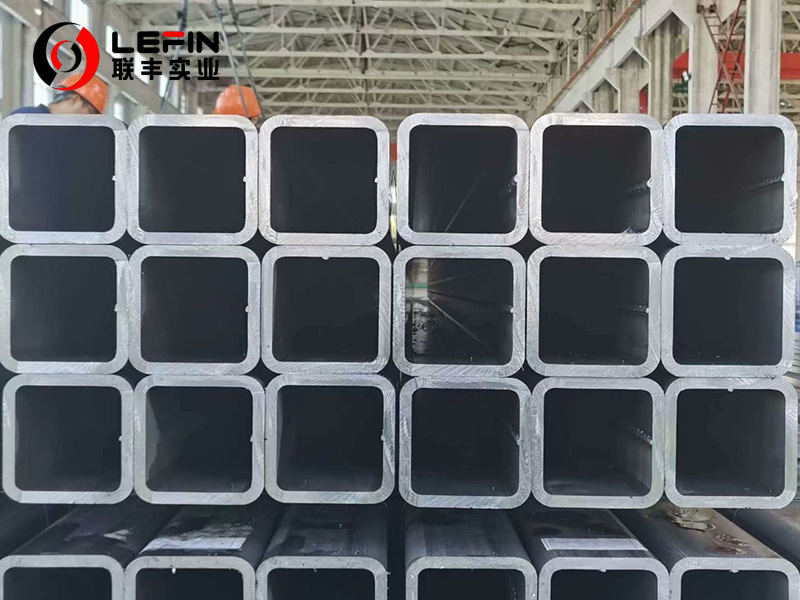
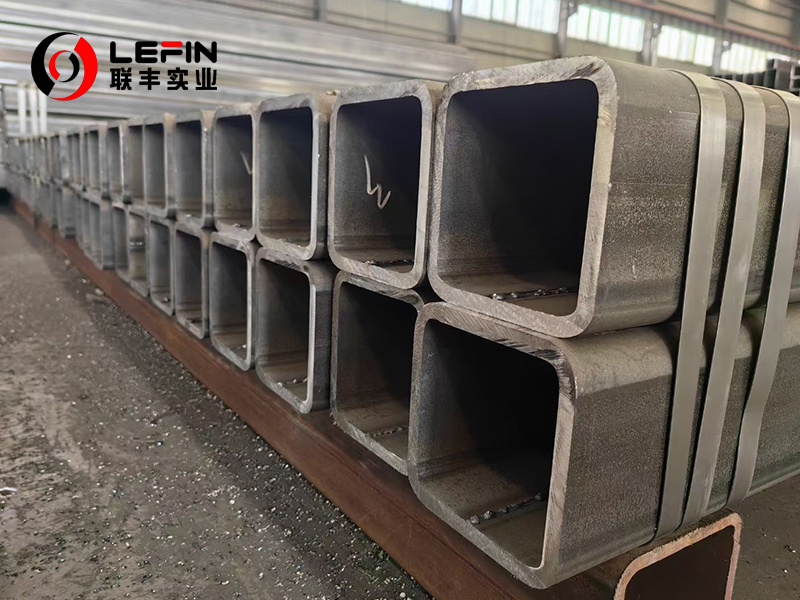



S355 Grade Steel Hollow Sections
Subcategory
Keyword
- Details
-
General Overview
S355 is a European structural steel grade with a minimum yield strength of 355 MPa at ≤16mm thickness.Subgrades (JR, J0H, J2H) indicate impact toughness requirements at different temperatures:
S355JR: Room temperature (20°C impact test).
S355J0H: 0°C impact test.
S355J2H: -20°C impact test.
The "H" in J0H/J2H denotes hollow sections (applies to EN 10219 cold-formed pipes).
Key Differences: EN 10210 Vs. EN 10219
Parameter
EN 10210 (Hot-Finished)
EN 10219 (Cold-Formed)
Manufacturing
Hot-formed, seamless or welded.
Cold-formed, welded (from coiled sheet).
Dimensional Tolerance
Tighter tolerances (better surface finish).
Slightly looser tolerances.
Mechanical Properties
Higher ductility (hot-working preserves grain structure).
Slightly lower ductility (cold-work hardening).
Impact Toughness
Generally better due to hot-forming process.
May require stricter testing for cold-formed variants.
Applications
Heavy-load structures (e.g., bridges, buildings).
Light-to-medium load (e.g., frames, supports).

Chemical Composition (Common For All S355 Grades)
Carbon (C): ≤0.22%.
Silicon (Si): ≤0.55%.
Manganese (Mn): ≤1.60%.
Phosphorus (P):EN 10210: ≤0.035%(J0H), ≤0.030%(J2H);
EN 10219: ≤0.040%(J0H), ≤0.035%(J2H);
Sulfur (S):
EN 10210: ≤0.035%(J0H), ≤0.030%(J2H);
EN 10219: ≤0.040%(J0H), ≤0.035%(J2H);
Micro alloys (Nb, V, Ti): Optional for grain refinement (especially in J2H).
Note: Both EN 10210 (hot-finished) and EN 10219 (cold-formed) S355 steel pipes have similar carbon, manganese, and impurity limits. However, EN 10219 may require stricter control of residuals (e.g., nitrogen) for better cold-forming.
Mechanical Properties (Typical Values)Grade
Yield Strength (MPa)
Nominal thickness≤16mmTensile Strength (MPa)
Nominal thickness >3≤40Elongation (%)
Nominal thickness≤40mmImpact Energy (J)
S355JR
≥355
470–630 (EN10210)
490–630 (EN10219)
≥22 (EN10210)
≥20 (EN10219)
≥27 J at 20°C
S355J0H
≥355
470–630 (EN10210)
490–630 (EN10219)
≥22 (EN10210)
≥20 (EN10219)
≥27 J at 0°C
S355J2H
≥355
470–630 (EN10210)
490–630 (EN10219)
≥22 (EN10210)
≥20 (EN10219)
≥27 J at -20°C
Note: EN 10210 offers higher ductility due to hot-forming, while EN 10219 has slightly higher strength from cold-work hardening. EN 10219 also includes low-temperature grades (J0H/J2H) for cold climates.
Hot vs. Cold Differences:
● Hot-finished (EN 10210): Typically show higher elongation (better ductility), better for heavy loads.● Cold-formed (EN 10219): More cost-effective, have higher tensile strength with options for cold resistance.

Applications And Advantages
EN 10210 Hot-Finished Pipes:
● Applications: Critical structural components (building frames, bridges, offshore platforms), heavy machinery, and high-stress welded constructions.
● Advantages:
Excellent weldability and formability due to homogeneous microstructureSuperior fatigue resistance and fracture toughness
Better dimensional accuracy and surface finish
Ideal for dynamic loading conditions
EN 10219 Cold-Formed Pipes:
● Applications: Light-to-medium structural applications (scaffolding, storage racks, agricultural equipment), architectural elements, and cost-sensitive projects.
● Advantages:
Higher yield strength from cold-workingMore economical for mass production
Available in precise, complex cross-sections
Low-temperature grades (J0H/J2H) perform well in cold climates

Summary And Selection Guidelines
S355-grade steel pipes under EN 10210 (hot-finished) and EN 10219 (cold-formed) standards offer distinct advantages tailored to different structural requirements.● EN 10210 pipes excel in heavy-load, high-integrity applications due to their superior ductility, impact toughness, and weldability from the hot-forming process. They are the preferred choice for critical structures like bridges, high-rise buildings, and offshore platforms where dynamic loading and fatigue resistance are crucial.
● EN 10219 pipes, on the other hand, provide cost-effective solutions for light-to-medium structural applications, with the added benefit of cold-work-enhanced strength and specialized low-temperature grades (J0H/J2H). Their precise forming capabilities make them ideal for architectural elements, storage systems, and projects requiring complex cross-sections.
Key Selection Criteria:
● Choose EN 10210 when structural integrity, weld performance, and dynamic load resistance are priorities.
● Opt for EN 10219 for budget-conscious projects, standardized components, or cold-environment applications.
Both standards maintain the core S355 mechanical properties but optimize them for different manufacturing processes and end uses, allowing engineers to select the most appropriate solution based on project-specific demands.



Related products
Product Consulting

Address: Hengtai Road,Daqiuzhuang Town,Jinghai County,Tianjin,China
Mob: +8615122229899(whatspp)
Phone: +86 22 58171905
Fax: +86 22 58171902
E-mail:info@lefinsteel.com
Get company updates

Tianjin Lefin Industrial Co.,Ltd. All rights reserved City sub-station SEO www.300.cn

