



- Details
-
AS 1163 C350 steel pipe is a type of cold-formed electric resistance welded (ERW) hollow structural steel pipe. It is widely used in various structural applications due to its excellent mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness.
Basic Characteristics
Manufacturing Process: AS 1163 C350 steel pipes are produced through a cold-formed process, which involves rolling steel sheets into the desired shape and then welding the seam using electric resistance welding.Grade Classification: The "C350" in AS 1163 C350 indicates that the steel has a minimum yield strength of 350 MPa. The prefix "C" signifies that the steel is cold-formed.
Chemical Composition
AS 1163 C350 steel is a carbon-manganese steel with controlled amounts of alloying elements to achieve its mechanical properties. The key elements and their maximum limits are:CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
Grades (see Note 1)
Chemical Composition (cast or product analysis) (see Note 2) % max.
C
Si
Mn
P
S
Cr
Mo
Al (see Note 3)
Ti
Micro-alloying elements
CE (see Note 4)
C350, C350L0
0.20
0.25
1.60
0.03
0.03
0.30
0.10
0.10
0.04
0.15 (see Note 6)
0.43
NOTES:
1 The use of sulphide modification manufacturing techniques for these grades is permitted .
2 The following elements may be present to the limits stated:
(a) Copper 0.25% .
(b) Nickel 0.25% .
3 Limits specified are for soluble or total aluminum .
4 Carbon equivalent (CE) is calculated from the following equation:
5 Applies to niobium and vanadium only . However, niobium greater than 0.010% is not permitted.
6 Applies to niobium, vanadium and titanium only . However, vanadium greater than 0. 10% is not permitted .
7 For circular hollow sections (CHS), the silicon limit shall be 0.45.
Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties of the AS/NZS 1163 steel pipe are particularly critical. During the production process, we ensure that each pipe meets the parameters of tensile strength, yield strength and elongation AS/NZS 1163. Ensure the bearing capacity and stability of each steel pipe.TENSILE TEST REQUIREMENTS
Grade
Minimum Yield StrengthMPa
Minimum Tensile StrengthMPa
Minimum Elongation as a Proportion of The Gauge Length of 5.65√So (see Note) %
Circular Hollow Sections do/t
Rectangular Hollow Sections b/t, d/t
≤15
>15≤ 30
>30
≤15
>15 ≤30
>30
C350, C350L0
350
430
16
18
20
12
14
16
NOTE:These limits apply to the face from which the tensile test is taken. That is, for RHS, the use of b/t or d/t ratio is dependent on which face the test specimen is cut from. For SHS, there is only one ratio (as b = d). CHARPY V-NOTCH IMPACT TEST REQUIREMENTS
Grade
Test temperature°C
Minimum absorbed energy, J
Size of test piece
10 mm × 10 mm
10 mm × 7.5 mm
10 mm × 5 mm
Average of 3 tests
Individual test
Average of 3 tests
Individual test
Average of 3 tests
Individual test
C350L0
0
27
20
22
16
18
13
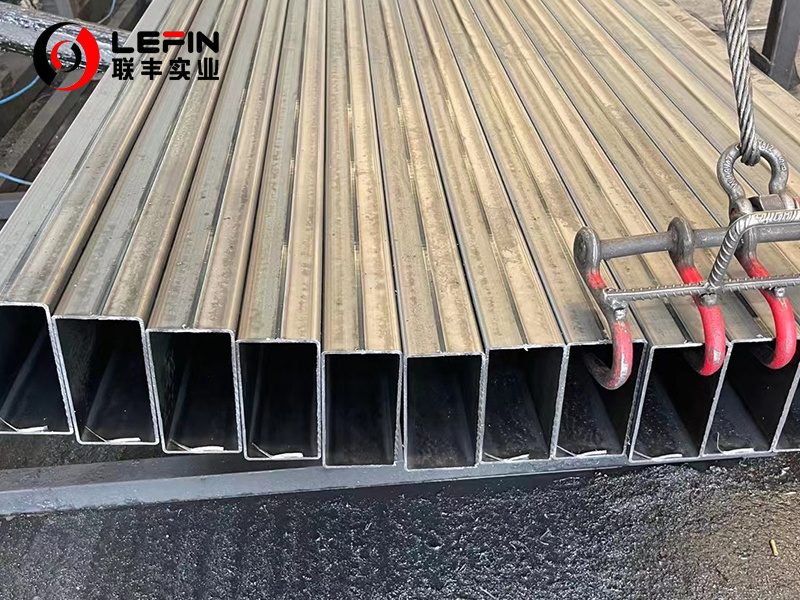

Dimensions & Tolerances
The standard AS/NZS 1163 specifies several common shapes of steel pipes, including round, square and rectangular.Round steel pipe: Round steel pipe smooth section, easy to connect and install, suitable for a variety of structural projects, because it can evenly distribute pressure, ensuring strong compression and bending resistance.
Square steel pipe: with a regular square cross-section, square steel pipe is convenient for positioning and fixing, and its excellent torsional and flexural properties make it perform well in occasions where lateral forces are required.
Rectangular steel pipe: the length and width can be flexibly adjusted according to actual needs to meet diverse design needs, especially suitable for structural systems that need to withstand specific directional forces.TOLERANCES FOR SHAPE AND MASS
Characteristic
Circular hollow sections
Square and rectangular hollow sections
External dimensions (do, d and b)
±1%, with a minimum of ±0.5 mm and a maximum of ±10 mm
±1%, with minimum of +0.5 mm, -0.5mm
Thickness (t)
For do £ 406.4 mm: ±10% For do > 406.4 mm: ±10% with a max of ±2 mm
+10%. -10%
Out-of-roundness (o)
±2% for hollow sections having a diameter to thickness ratio not exceeding 100 (see Note 1)
–
Concavity/convexity (see Note 2)
–
Max. 0.8% or 0.5 mm, whichever is greater
Squareness of sides
–
90°±1°
External corner profile
See Table 5
Twist (v)
–
2 mm + 0.5 mm/m length
Straightness (see Note 3)
0.20% of total length
0.15% of total length

Applications And Advantages
Applications
Due to its balanced properties, AS 1163 C350 steel pipe is suitable for a wide range of applications, including:Structural Engineering: Used in commercial buildings, bridges, industrial facilities, and infrastructure projects such as transmission towers.
General Construction: Ideal for frameworks, columns, beams, scaffolding, and other structural components.
Other Uses: Also used in furniture, handrails, and display stands.
Advantages
Cost-Effectiveness: AS 1163 C350 provides a good balance between strength and cost, making it an economical choice for many projects.
Versatility: It is suitable for both light and medium structural loads.
Availability: As one of the most commonly used grades, it is readily available in the market.
Durability: The steel offers excellent resistance to wear and tear, ensuring long-term performance.
Comparison With Other Grades
Compared to other grades in the AS 1163 standard:C250: AS 1163 C350 has higher strength (350 MPa yield strength vs. 250 MPa for C250) and greater load-bearing capacity.
C450: While C450 provides even higher strength (450 MPa yield strength), C350 offers better ductility and is often more cost-effective.
Summary
AS 1163 C350 steel pipe is a high-strength (350 MPa yield) structural pipe, available in welded or seamless forms. Widely used in construction and engineering, it meets Australian standards for durability and weldability. Optional coatings enhance corrosion resistance, making it ideal for infrastructure and mechanical applications.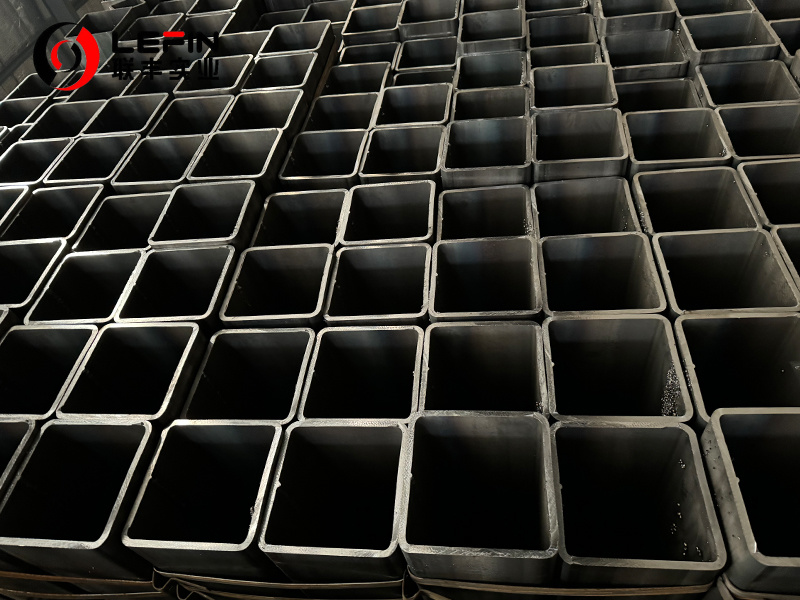
AS 1163 C350 steel pipe
Subcategory
Keyword
- Details
-
AS 1163 C350 steel pipe is a type of cold-formed electric resistance welded (ERW) hollow structural steel pipe. It is widely used in various structural applications due to its excellent mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness.
Basic Characteristics
Manufacturing Process: AS 1163 C350 steel pipes are produced through a cold-formed process, which involves rolling steel sheets into the desired shape and then welding the seam using electric resistance welding.Grade Classification: The "C350" in AS 1163 C350 indicates that the steel has a minimum yield strength of 350 MPa. The prefix "C" signifies that the steel is cold-formed.
Chemical Composition
AS 1163 C350 steel is a carbon-manganese steel with controlled amounts of alloying elements to achieve its mechanical properties. The key elements and their maximum limits are:CHEMICAL COMPOSITION
Grades (see Note 1)
Chemical Composition (cast or product analysis) (see Note 2) % max.
C
Si
Mn
P
S
Cr
Mo
Al (see Note 3)
Ti
Micro-alloying elements
CE (see Note 4)
C350, C350L0
0.20
0.25
1.60
0.03
0.03
0.30
0.10
0.10
0.04
0.15 (see Note 6)
0.43
NOTES:
1 The use of sulphide modification manufacturing techniques for these grades is permitted .
2 The following elements may be present to the limits stated:
(a) Copper 0.25% .
(b) Nickel 0.25% .
3 Limits specified are for soluble or total aluminum .
4 Carbon equivalent (CE) is calculated from the following equation:
5 Applies to niobium and vanadium only . However, niobium greater than 0.010% is not permitted.
6 Applies to niobium, vanadium and titanium only . However, vanadium greater than 0. 10% is not permitted .
7 For circular hollow sections (CHS), the silicon limit shall be 0.45.
Mechanical Properties
The mechanical properties of the AS/NZS 1163 steel pipe are particularly critical. During the production process, we ensure that each pipe meets the parameters of tensile strength, yield strength and elongation AS/NZS 1163. Ensure the bearing capacity and stability of each steel pipe.TENSILE TEST REQUIREMENTS
Grade
Minimum Yield StrengthMPa
Minimum Tensile StrengthMPa
Minimum Elongation as a Proportion of The Gauge Length of 5.65√So (see Note) %
Circular Hollow Sections do/t
Rectangular Hollow Sections b/t, d/t
≤15
>15≤ 30
>30
≤15
>15 ≤30
>30
C350, C350L0
350
430
16
18
20
12
14
16
NOTE:These limits apply to the face from which the tensile test is taken. That is, for RHS, the use of b/t or d/t ratio is dependent on which face the test specimen is cut from. For SHS, there is only one ratio (as b = d). CHARPY V-NOTCH IMPACT TEST REQUIREMENTS
Grade
Test temperature°C
Minimum absorbed energy, J
Size of test piece
10 mm × 10 mm
10 mm × 7.5 mm
10 mm × 5 mm
Average of 3 tests
Individual test
Average of 3 tests
Individual test
Average of 3 tests
Individual test
C350L0
0
27
20
22
16
18
13

Dimensions & Tolerances
The standard AS/NZS 1163 specifies several common shapes of steel pipes, including round, square and rectangular.Round steel pipe: Round steel pipe smooth section, easy to connect and install, suitable for a variety of structural projects, because it can evenly distribute pressure, ensuring strong compression and bending resistance.
Square steel pipe: with a regular square cross-section, square steel pipe is convenient for positioning and fixing, and its excellent torsional and flexural properties make it perform well in occasions where lateral forces are required.
Rectangular steel pipe: the length and width can be flexibly adjusted according to actual needs to meet diverse design needs, especially suitable for structural systems that need to withstand specific directional forces.TOLERANCES FOR SHAPE AND MASS
Characteristic
Circular hollow sections
Square and rectangular hollow sections
External dimensions (do, d and b)
±1%, with a minimum of ±0.5 mm and a maximum of ±10 mm
±1%, with minimum of +0.5 mm, -0.5mm
Thickness (t)
For do £ 406.4 mm: ±10% For do > 406.4 mm: ±10% with a max of ±2 mm
+10%. -10%
Out-of-roundness (o)
±2% for hollow sections having a diameter to thickness ratio not exceeding 100 (see Note 1)
–
Concavity/convexity (see Note 2)
–
Max. 0.8% or 0.5 mm, whichever is greater
Squareness of sides
–
90°±1°
External corner profile
See Table 5
Twist (v)
–
2 mm + 0.5 mm/m length
Straightness (see Note 3)
0.20% of total length
0.15% of total length

Applications And Advantages
Applications
Due to its balanced properties, AS 1163 C350 steel pipe is suitable for a wide range of applications, including:Structural Engineering: Used in commercial buildings, bridges, industrial facilities, and infrastructure projects such as transmission towers.
General Construction: Ideal for frameworks, columns, beams, scaffolding, and other structural components.
Other Uses: Also used in furniture, handrails, and display stands.
Advantages
Cost-Effectiveness: AS 1163 C350 provides a good balance between strength and cost, making it an economical choice for many projects.
Versatility: It is suitable for both light and medium structural loads.
Availability: As one of the most commonly used grades, it is readily available in the market.
Durability: The steel offers excellent resistance to wear and tear, ensuring long-term performance.
Comparison With Other Grades
Compared to other grades in the AS 1163 standard:C250: AS 1163 C350 has higher strength (350 MPa yield strength vs. 250 MPa for C250) and greater load-bearing capacity.
C450: While C450 provides even higher strength (450 MPa yield strength), C350 offers better ductility and is often more cost-effective.
Summary
AS 1163 C350 steel pipe is a high-strength (350 MPa yield) structural pipe, available in welded or seamless forms. Widely used in construction and engineering, it meets Australian standards for durability and weldability. Optional coatings enhance corrosion resistance, making it ideal for infrastructure and mechanical applications.

Related products
Product Consulting

Address: Hengtai Road,Daqiuzhuang Town,Jinghai County,Tianjin,China
Mob: +8615122229899(whatspp)
Phone: +86 22 58171905
Fax: +86 22 58171902
E-mail:info@lefinsteel.com
Get company updates

Tianjin Lefin Industrial Co.,Ltd. All rights reserved City sub-station SEO www.300.cn

