






- Details
-
Large Diameter Hollow Structural Sections (HDS) are a kind of tubular materials widely used in engineering structures, which have the characteristics of high strength, light weight, excellent bending and torsional resistance
Definition and classification
1. Basic definition
The large-diameter hollow section pipe refers to the pipe with a large outer diameter (usually ≥300mm) and a hollow section, and the section shape includes:
• Circular Hollow Section (CHS, Circular Hollow Section) : Best torsional resistance, low fluid resistance.
• Square Hollow Section (SHS) : High flexural stiffness for easy connection.
• Rectangular Hollow Section (RHS) : Advantages of bending resistance and space utilization. - Oval or polygon: specially designed to meet specific needs.2. Size range
• Outer diameter: usually more than 300mm, up to several meters (such as tubes for offshore platforms).
• Wall thickness: from a few millimeters to tens of millimeters depending on the load requirements.Our products
Standard: BS EN 10210,BS EN 10219,BS EN 10217,
ASTM A500,ASTM A501,ASTM A53,ASTM A253
GB/T 3094,GB/T 6728
JIS G3466,JIS G3101
AS 1163API 5L
Size:
(SHS)OD:20*20-1200*1200mm WT: 1.2mm-60mm
(RHS)OD:20*30-1200*1500mm WT: 1.2-60mm
(CHS)ERW:OD:1/2inch - 24inch WT:21.3-610mm
(CHS)LSAW:OD:406-1420mm WT:8-60mm
(CHS)SSAW:OD:219-4020mm WT:5-25.4mm
Length:4m, 6m, 12m or as your required
Corner Type: Radius Corner,Sharp Angle Corner, Right Angle Corner
Application: Heavy steel structure, Aerospace Engineering, High-speed rail,Shipbuilding, For machinery, For automobiles and high-speed trains, For chemical industry and boiler, For bridge.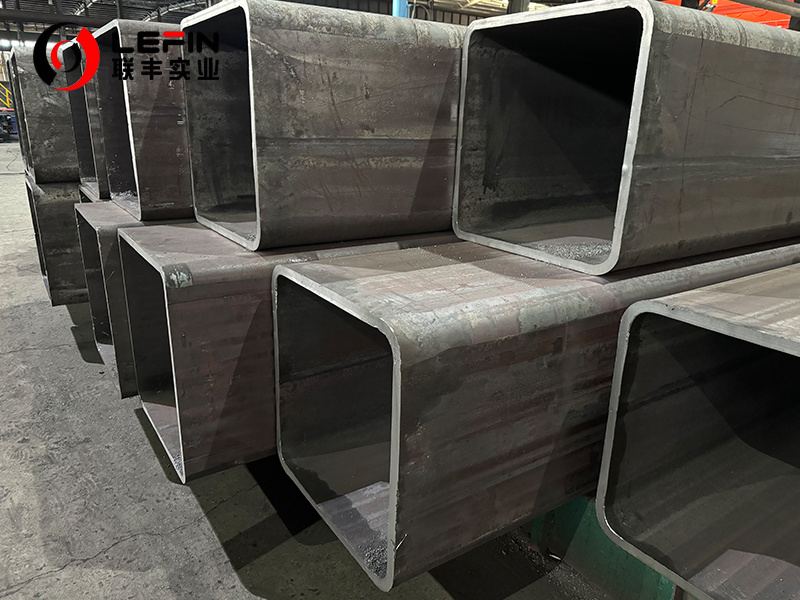
Materials and manufacturing process
1. Commonly used materials
Carbon steel: Low cost, high strength, suitable for buildings and Bridges (e.g. Q235, Q355).
• Stainless steel: strong corrosion resistance, used in Marine engineering or chemical environment.
• Aluminum alloy: lightweight demand scenarios (such as aerospace).
Composite materials: such as carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP) for high-end structures.2. Manufacturing process
• Hot rolling molding: through high temperature rolled steel plate crimped welding, suitable for mass production.
• Cold forming: welding after bending steel plate at room temperature, high precision but high cost.
• Spiral welding/straight seam welding: The welding method affects the uniformity and strength of the pipe.
• Extrusion (aluminum/composite) : suitable for complex cross sections or high precision requirements.Structural characteristics and advantages
1. Mechanical properties
• Hollow section has a high section moment of inertia, excellent bending and torsional resistance.
• Uniform closed section reduces stress concentration and provides long fatigue life.2. Lightweight and efficient
• Hollow structure saves material and can reduce weight by 30%-50% compared to solid structure.
• The interior space can be lined or filled with concrete (e.g. CFST, concrete-filled steel tube structure).3. Versatility
• The surface is easy to be coated with anti-corrosion layer and adapt to harsh environment (such as Marine salt spray, chemical corrosion).
• Can be designed as modular components for quick installation.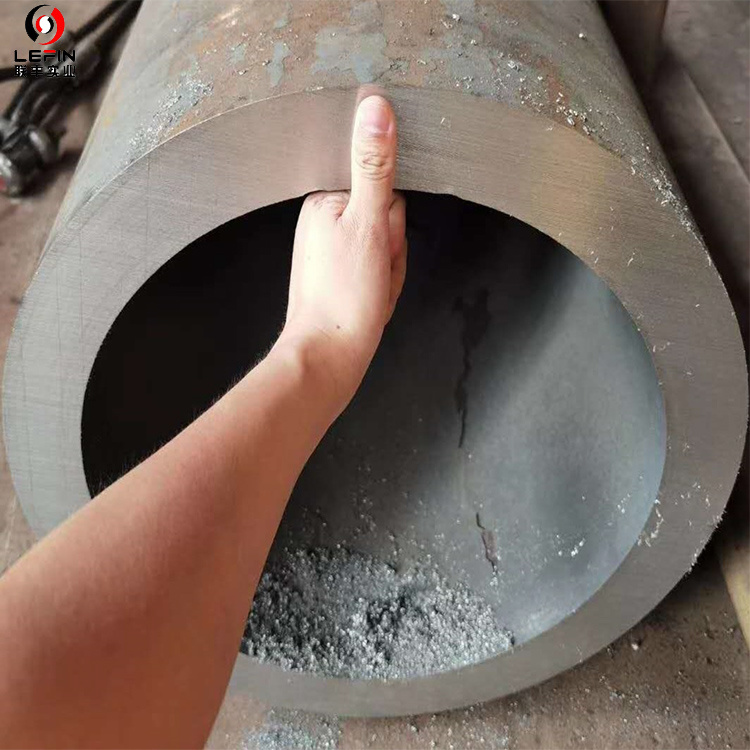
Typical application areas
1. Buildings and Bridges
• High-rise building core tube, long-span truss, bridge main beam (such as Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge).
Concrete-filled steel tube columns (CFST) combine the advantages of steel and concrete.2. Ocean engineering
• Offshore platform support structure, submarine pipeline, floating structure.3. Machinery and transportation
• Heavy mechanical arms, crane trusses, vehicle chassis frames.4. Energy and Municipal services
• Wind power tower, water pipeline, underground integrated pipe gallery.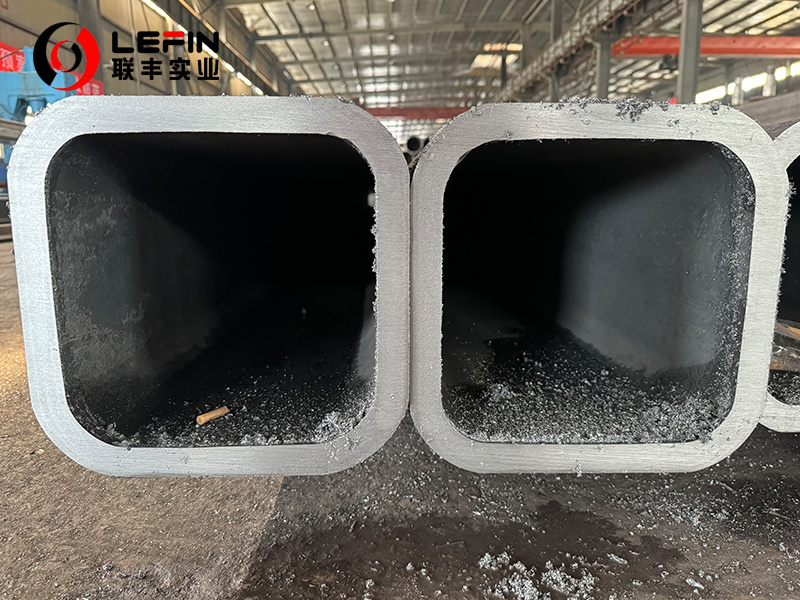
Challenges and limitations
1. Production and transportation
• Large diameter pipe production equipment has high requirements, and the welding process needs strict quality control.
• Transportation and lifting require special equipment and high costs.2. Local stability problem
• Thin-walled tubes may suffer local buckling under pressure, which needs to be solved by stiffening or increasing wall thickness.3. Anti-corrosion maintenance
• Regular inspection of coatings or cathodic protection in long-term exposure environments.Sum up
Large diameter hollow section pipe has become a key material in modern engineering due to its excellent mechanical properties and versatility. With the progress of material science and manufacturing technology, its application potential in super-span structures, deep-sea engineering and other fields will be further released. Load conditions, environmental factors and economy should be considered comprehensively in selecting suitable pipes.
LARGE DIAMETER HOLLOW SECTION
Subcategory
Keyword
- Details
-
Large Diameter Hollow Structural Sections (HDS) are a kind of tubular materials widely used in engineering structures, which have the characteristics of high strength, light weight, excellent bending and torsional resistance
Definition and classification
1. Basic definition
The large-diameter hollow section pipe refers to the pipe with a large outer diameter (usually ≥300mm) and a hollow section, and the section shape includes:
• Circular Hollow Section (CHS, Circular Hollow Section) : Best torsional resistance, low fluid resistance.
• Square Hollow Section (SHS) : High flexural stiffness for easy connection.
• Rectangular Hollow Section (RHS) : Advantages of bending resistance and space utilization. - Oval or polygon: specially designed to meet specific needs.2. Size range
• Outer diameter: usually more than 300mm, up to several meters (such as tubes for offshore platforms).
• Wall thickness: from a few millimeters to tens of millimeters depending on the load requirements.Our products
Standard: BS EN 10210,BS EN 10219,BS EN 10217,
ASTM A500,ASTM A501,ASTM A53,ASTM A253
GB/T 3094,GB/T 6728
JIS G3466,JIS G3101
AS 1163API 5L
Size:
(SHS)OD:20*20-1200*1200mm WT: 1.2mm-60mm
(RHS)OD:20*30-1200*1500mm WT: 1.2-60mm
(CHS)ERW:OD:1/2inch - 24inch WT:21.3-610mm
(CHS)LSAW:OD:406-1420mm WT:8-60mm
(CHS)SSAW:OD:219-4020mm WT:5-25.4mm
Length:4m, 6m, 12m or as your required
Corner Type: Radius Corner,Sharp Angle Corner, Right Angle Corner
Application: Heavy steel structure, Aerospace Engineering, High-speed rail,Shipbuilding, For machinery, For automobiles and high-speed trains, For chemical industry and boiler, For bridge.
Materials and manufacturing process
1. Commonly used materials
Carbon steel: Low cost, high strength, suitable for buildings and Bridges (e.g. Q235, Q355).
• Stainless steel: strong corrosion resistance, used in Marine engineering or chemical environment.
• Aluminum alloy: lightweight demand scenarios (such as aerospace).
Composite materials: such as carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP) for high-end structures.2. Manufacturing process
• Hot rolling molding: through high temperature rolled steel plate crimped welding, suitable for mass production.
• Cold forming: welding after bending steel plate at room temperature, high precision but high cost.
• Spiral welding/straight seam welding: The welding method affects the uniformity and strength of the pipe.
• Extrusion (aluminum/composite) : suitable for complex cross sections or high precision requirements.Structural characteristics and advantages
1. Mechanical properties
• Hollow section has a high section moment of inertia, excellent bending and torsional resistance.
• Uniform closed section reduces stress concentration and provides long fatigue life.2. Lightweight and efficient
• Hollow structure saves material and can reduce weight by 30%-50% compared to solid structure.
• The interior space can be lined or filled with concrete (e.g. CFST, concrete-filled steel tube structure).3. Versatility
• The surface is easy to be coated with anti-corrosion layer and adapt to harsh environment (such as Marine salt spray, chemical corrosion).
• Can be designed as modular components for quick installation.
Typical application areas
1. Buildings and Bridges
• High-rise building core tube, long-span truss, bridge main beam (such as Hong Kong-Zhuhai-Macao Bridge).
Concrete-filled steel tube columns (CFST) combine the advantages of steel and concrete.2. Ocean engineering
• Offshore platform support structure, submarine pipeline, floating structure.3. Machinery and transportation
• Heavy mechanical arms, crane trusses, vehicle chassis frames.4. Energy and Municipal services
• Wind power tower, water pipeline, underground integrated pipe gallery.
Challenges and limitations
1. Production and transportation
• Large diameter pipe production equipment has high requirements, and the welding process needs strict quality control.
• Transportation and lifting require special equipment and high costs.2. Local stability problem
• Thin-walled tubes may suffer local buckling under pressure, which needs to be solved by stiffening or increasing wall thickness.3. Anti-corrosion maintenance
• Regular inspection of coatings or cathodic protection in long-term exposure environments.Sum up
Large diameter hollow section pipe has become a key material in modern engineering due to its excellent mechanical properties and versatility. With the progress of material science and manufacturing technology, its application potential in super-span structures, deep-sea engineering and other fields will be further released. Load conditions, environmental factors and economy should be considered comprehensively in selecting suitable pipes.
Related products
Product Consulting

Address: Hengtai Road,Daqiuzhuang Town,Jinghai County,Tianjin,China
Mob: +8615122229899(whatspp)
Phone: +86 22 58171905
Fax: +86 22 58171902
E-mail:info@lefinsteel.com
Get company updates

Tianjin Lefin Industrial Co.,Ltd. All rights reserved City sub-station SEO www.300.cn

